Table of Contents
Introduction
This article will give you an idea about how to use CASE expression in T-SQL or as a formula of a particular column.
What is CASE Expression
CASE is the special scalar expression in SQL language. CASE expression is widely used to facilitate determining / setting a new value from user input values. CASE expression can be used for various purposes which depends on the business logic.
CASE expression is mostly used in SQL stored procedure or as a formula for a particular column, which optimizes the SQL statements.
Syntax of CASE Expression
SQL CASE expression is used as a type of IF-THEN-ELSE statement. It is similar to switch statement in recent programming languages such as C# and Java. The syntax of the CASE statement is simple as follows:
1. CASE column_name
2. WHEN condition1 THEN result1
3. WHEN condition2 THEN result2
4. ...
5. ELSE result
6. END
Sample Example of CASE Statement
DECLARE @intInput INT
SET @intInput = 2
SELECT CASE(@intInput) WHEN 1 THEN 'One' WHEN 2 THEN 'Two' _
WHEN 3 THEN 'Three' ELSE 'Your message.' END
Use of CASE Expression
The case expression can be used anywhere scalar expressions are allowed, including in WHERE and HAVING clauses of the select statement.
In this article, I would like to show the most commonly used case expression in:
- Stored procedure
- Formula of a particular column
- View
Basic Use in a Stored Procedure
A simple example of using CASE in a stored procedure is given below:
ALTER PROCEDURE [dbo].[spGetCountry]
@intCode INT
,@varOutPut VARCHAR(100) OUTPUT
AS
BEGIN
SELECT CASE(@intCode) WHEN 1 THEN 'Country_1'
WHEN 2 THEN 'Country_2'
WHEN 3 THEN 'Country_3'
WHEN 4 THEN 'Country_4'
WHEN 5 THEN 'Country_5'
WHEN 6 THEN 'Country_6'
WHEN 7 THEN 'Country_7'
WHEN 8 THEN 'Country_8'
WHEN 9 THEN 'Country_9'
WHEN 10 THEN 'Country_10'
ELSE 'Unknown' END
END
Basic Use in a Table Column Formula
When we create a Table in design mode, SQL server provides us the properties of each column, where we can set various property values like a default value of a column, identity of a column, etc. Every column has a special property that is a custom formula, where you can set your own formula for data manipulation. Let’s take an example:
Our target is to write a formula for a column, and this formula is responsible for setting a new value for another column.
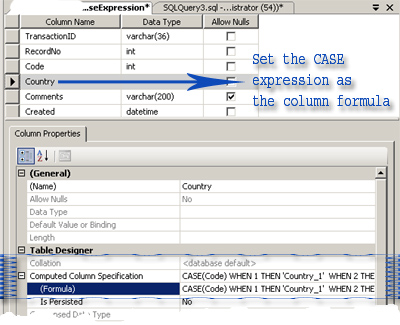
Figure 1 - How we can set a formula for a particular column
A simple example of using CASE in a Table column formula is given below:
// SQL CASE statement
(case [Code] when (1) then 'Country_1' when (2) then 'Country_2' _
when (3) then 'Country_3' when (4) then 'Country_4' when (5) _
then 'Country_5' when (6) then 'Country_6' when (7) then 'Country_7' _
when (8) then 'Country_8' when (9) then 'Country_9' when (10) _
then 'Country_10' else 'Unknown' end)
When you insert / update a value at column “code”, the SQL server will fire the formula which is associated with the column “code” and finally set the value of that particular column.

Figure 2 - How column "Country" sets value when column code value is inserted / updated
Basic Use in a View
There is nothing new to use CASE expression in a view object. As I mentioned before, CASE expression can be used anywhere scalar expressions are allowed, including in WHERE and HAVING clauses of the select statement.
Conclusion
I hope that you will get an idea about how to use CASE expression. Enjoy!
History
- 18th August 2009: Initial post
A well experienced leader with successful track record of software development, product innovations, brand management and corporate communication etc. Some successful product innovations have also achieved and awards “Most Valuable Professional” (MVP) at 2010 and 2011 by codeproject.com and also selected as a mentor of codeproject.com. Published over 100 technical articles in various software development resource sites (i.e., codeprojetc.com, Microsoft MSDN, and IEEE & IBM (In progress)) and various IT Forums, Blogs etc.
Over fourteen years of professional experiences in ICT field having extensive experience in formulating corporate vision and long term strategy. Leading development related functions including design, development, services, data management and analytics, customer experience management, content services, digital analytics and optimization.I have also more than two years’ of strong experience in mobile-VAS (platform development).
An individual with results-driven approach and relentless in pursuit of excellence from a business and organizational standpoint.Honest, believes in transparency, commitment and teamwork.
Expertise: Software/Solution Architect, Technical Research, MIS, Data Analytics, Data Mining, BI, SaaS platform base application development, Large scale Win32 Form/Web based business software solutions, Security, Enterprise applications development, integration, etc.
Technologies/Tools: Microsoft.Net, Microsoft SQL Server , Oracle, MySQL, ETL, Visual C#, VB.NET, ASP.NET, , Python, Java, API, MVC, Cloud Computing, SaaS, Open FaaS, AWS,AWS Lambda, MS Azure, WebAPI , WPF, WCF, PHP, Microsoft Power BI, SPSS, PS2, R, Add-In, Visual Basic etc.
.Net UI component: Telerik, DevExpress, Ext.Net etc.
Scripting language: JavaScript, AngularJS, node.JS etc.
Source control / Subversion: Git, Smart SVN, Assembla etc.
Development methodologies: Agile,RAD etc.
Project Management / Issues Tracking Tools: JIRA, Trello, Slack, Clockingit etc.
